The marine industry has played a dominant role in the expansion of trade over years. Shipping has been the most effective mode of trading leaving a remarkable influence on the world economy.
For centuries, companies have shipped cargo in various forms effortlessly. However, with the growing population, EXIM (Export and Import) have increased exponentially in the global markets and this escalation is expected to continue for quite a long time.
Maritime trading companies have always used conventional methods of shipping and correspondence, such as bulk carriers, cargo ships, radio signals, and more. These days, however, with the advent of revolutionary technologies and ideas, it has become imperative for the trade industries to adopt new technological trends for providing an even faster and more efficient trade service.
With the advancement in technology there are number of methods that ensure an up gradation in the overall operation of the shipping industry have been introduced. The mega ships, robots replacing human, new and advanced materials, alternative fuels are all set to bring a drastic change in the marine industry.
The requirement of commercial marketplace, so that it can become more competitive and cost-effective. Shipping is an industry which is constantly being affected by global trends and by advancement in the technologies, materials and fuels. Here are few trends that are perfectly illustrating some of the dynamic changes that are happening in the shipping industry and the new opportunities that these create for the following sector.
-
Digital sensoring
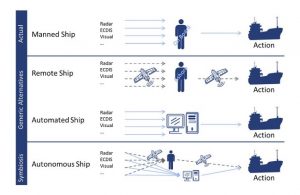
The technology for monitoring ship operations and performance has been firmly increasing in its sophistication. The future ships will have an entire network of sensors for measurement of all the aspects of operations, including detection of faults and identifying various areas demanding maintenance or repair. Allied to this, increasingly powerful ship to shore communications will mean that most of the aspects of ship’s operation can be regulated by a land-based team of fleet managers.
-
Bigger mega ships
The advancements in ship technology, structure and materials will lead to even bigger megaships, particularly within the container shipping industry. This huge ship will carry up to 20,150 TEU containers. Manufacturers will seek to take advantage of the lower transport costs that these vessels can provide by gearing their production to make the most efficient use of this container space.
-
Greener shipping
There is consistent pressure to lessen the carbon footprint of the world’s shipping fleets, and this is certainly increase in the future. A whole host of technologies are being analysed including low carbon fuels, more streamlined hulls, and more effective propeller design, upgraded sails planning to make savings on fuels, better hull coatings and even air cushions to lessen friction.
-
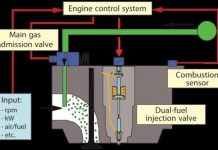
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) as fuel
There is raising interest in the potential of LNG as a fuel for commercial shipping. LNG is believed to be helpful for the operators in meeting their targets for reducing emissions, while also being competitive on price. CO2 emissions can be decreased by up to 25% when compared with diesel engines. While conventional oil-based fuels will continue to dominate in the coming years, there is likely to be raise in adoption of LNG for specialist vessels, which gives an opportunity for the technology to be proved and developed on a larger scale.
-
Robotic Automation
The usage of robots in every field has become quite common in the past few years. In the shipping, robots are slowly being used to aid all the tasks. Activities like packing, delivering, inspection, firefighting, etc. can be carried out by robots effortlessly. As robots work more efficiently and without any gap. These robots will also be able to detect and navigate ships. New model of robots, called ‘mini-robots’, are being mated with the sensors to recognize and note all the data in the ship and work on it. The manpower aboard ships will be considerably reduced.
-
Autonomous Ships
Autonomous systems in marine are acquiring immense recognition on account of their competence to deliver goods without any interference. These systems operate at high efficiency undoubtedly for a longer duration.
These are equipped with the current, advanced heat mapping and material detection technology, which eliminates the human effort involved.
-
IoT (Internet of Things)
IoT generally comprises of a GPS and a cloud-based database which collects all the data by devices on the ship. It also establishes a connection with the sensors, robots and other devices via a wireless work. It helps shipping industry in providing a better customer services.

-
The Rise of Smart Containers
2019 could be the year of extended use of smart containers in the industry as shipping has already begun to run trials of the various technologies. The industry is already witnessing the progress with Maersk disclosing its last year’s investments in inexpensive, disposable tracking devices, along with earlier initiatives to put sensors into its total 270,000 fleet of refrigerated boxes. Traxens intends to deploy 100,000 smart containers by the completion of 2019 counting MSC declaring, it will arm 50,000 dry cargo containers for smart container technology. In addition, to this CargoSmart is associated to over 40 ocean carriers to leading supply chain visibility.
-
Port Management
Expansion of operating methods at the harbour with the help of technology can lessen the waiting time of the various ships at the port, leading to less carbon emission from ships at the docks. The unloading of the ship to be done faster require usage of robots and other machinery to lift heavy cargo.
The vessels are getting huge and the biggest weigh more than 20 000 TEU carriers. The future, demands a wider spread of ports so as to make the cargo flow smoother without congestions. There is also a peril with only a few big ports regulating the logistics flows.
Conclusion
The increase in the usage of technology in shipping industry has its fair share of pros and cons. On one hand, it lessens the manual work and speeds up processes for better output and efficiency; but on the other hand, it constitutes increased security risks as well.
With the usage of internet in every apparatus of the ship, cyber security is of ultimate importance. Testing and routine data audits must be regular aboard the ships. Bulk data can be derived and stored in secure servers and examined. It is the accountability of software and the device developers to ensure that the apt security standards are upheld while integrating technology in various applications. Ship manufacturers and engineers also require to account for the growing technology in ships and modify ship design as and when needed.
Endnote
Technology and Shipping are no longer strangers. The technology hasn’t replaced manual involvement in shipping. The emerging trends in 2019 and the coming years should be seen as a valuable tool to assist shipping operations. All the available technology, if used appropriately and updated frequently, can assure much more able future for the shipping industry.