The Shipping Industry has left no stones unturned in order to tender best towards a greener marine environment.
Be it at manufacturing or at administrative levels, the maritime sector is taking advantage of the current technologies to assure that new ships contribute as low as possible to the global pollution. Designing a vessel in present era has become a challenging work, as these days a ship has to be fully complied with new environmental rules and regulations.
Green is presently the new fizz at the shipping ministry. The Indian government is planning to introduce perks for the “green ships” that enter the ports. Eventually, to reduce the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and thus limiting the damage to coastal life.
A few standard technologies have been developed so far to reach the ultimate goal of building a “Green ship” which would not only abide with the new environmental rules and regulations but on the other hand would also leave least possible carbon and sulfur foot-prints.
In an effort to reduce greenhouse gas emmissions, the government is striving for all ‘green’ ships docking at the nation’s ports. The ships require a minimum score with respect to fuel consumption and emissions including CO2, SOx and NOx.
GREEN PORTS ROUND THE WORLD
At some major ports like Hamburg in Germany, Antwerp in Belgium and Panama, the ministry has proposed offering a rebate of 25% on vessel related levies on such ships. To be entitled for a discount a vessel needs to score a minimum of 30 or more points on the International Environmental Shipping Index. This index rates vessels on a scale from 0 to 100 based on criteria such as fuel consumption and emissions including sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide.
With context to INDIA
Energy-efficiency and sustainability is presently the center of attention in the marine industry. The market for ‘green’ ships is growing rapidly and governments and companies are spending more for newly built vessels and also for developing existing ships to make them ‘greener’. Around 10% of ships entering India are ‘green ships’. As per the official estimates made in the year, 2017, 31,000 vessels dock at Indian ports. With vessel related charges nearing to Rs 12.97 lakh per ship, the total funds earned work out to Rs 4,000 crore. The 25% rebate offered, will imply a revenue loss of Rs 101 crore annually.
The Ministry of Shipping, with context to its ‘Green Port Initiative’ has been affirming on usage of renewable sources of energy to power Major Ports over the nation. The government aims to set up 91.50 MW of solar energy capacity at the twelve Major Ports and 45 MW of wind energy capacity by the two main Ports of Kandla and V. O. Chidambaranar. A few major Ports have begun the process of setting-up renewable energy projects by investing Rs.704.52 crores (Solar–Rs. 412.02 Cr and Wind–Rs. 292.50 Cr) in these.
Mundra Port
The wind energy projects will be accomplished by two Major Ports namely Kandla Port and V.O. Chidambaranar Port. The overall capacity of the wind energy projects is 45 MW out of which 6 MW has already been commissioned by Kandla Port. A total of 15.20 MW of solar projects has also been commissioned with Visakhapatnam Port leading the way with 9 MW, while the other ports in which solar projects have been commissioned are Kolkata Port (0.06 MW), New Mangalore Port (4.35 MW), V.O. Chidambaranar Port (0.5 MW), Mumbai Port (0.125 MW), Chennai Port (0.1 MW), Mormugao (0.24 MW) & JNPT (0.82 MW). The remaining solar power projects will be commissioned phase wise and is expected to be completed in near future.
It may be recalled that a MoU was endorsed between Indian Ports Association (IPA) and Solar Energy Corporation of India on the 15th of October, 2015 for the advancement of solar power projects at Major Ports. This is a new drive by Major Ports which has been taken in line with the ‘Green Port Initiative’ policy of the Government of India.
Project Green Ports covers few initiatives, such as preparation and monitoring plans, the acquisition of equipment required for monitoring environmental pollution and setting up sewage treatment plants.
On the basis of present scenario and the advancement of the technologies we have hereby, compiled a list of a few new technologies which if used together would lead in the ultimate Green Ship of the Future. Few of them are listed below:
- No Ballast System: Ballast water convention by IMO focuses on lowering the transit of sediments and microorganisms of one territory to another through the ballast of ships. For averting this condition, plans of making a “No Ballast Ships” is under process.
A no ballast ship or similar system can terribly reduce this problem. Read more about-“No Ballast ship” here.
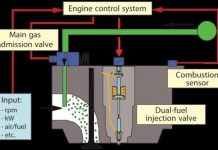
- LNG fuel is the future of the marine industry. LNG fuel helps in lessening of air pollution from vessels, and the components of LNG fuel with diesel oil will lead to efficient engine functioning, resulting in to the fuel saving.
- LNG Fuel for Auxiliary engine: Auxiliary engines on the vessels are main source of power. They are the machines that are continuous running onboard vessels. LNG fuel for such engines can drastically lessen air pollution occurred by the vessels.
- Sulphur Scrubber System: Usage of conventional fuel cannot be phased out from ships. Lessening the sulphur or SOx emission from the exhaust is a solution that would be used widely in the coming days. By the installation of an exhaust gas scrubber system wherein the sulphur is washed out from the exhaust gas of the engine resulting in deduction of SOx up to 98% along with other dangerous particles.
- Advanced Rudder and Propeller System: A well designed Propeller and streamlined rudder system can lessen the fuel consumption up to 4% leading in lesser emission. To reduce the fuel consumption and for the betterment of the speed of the ships the propeller and rudder systems have been developed.
- Speed Nozzle: The Speed Nozzles are mostly used in small supply vessels and tugs to provide power to the ships. With the new design features of merchant vessels, it can boost the propulsion efficiency of the ship by retaining power up to approx 5%.
- Hull Paint: Hull paint lessens the frictional resistance and thus resulting in to the savings of fuel upto 3-8%. It improves the emission of the vessel.
- Waste Heat Recovery System: Waste heat recovery system is already into the use in the sector. When putting it more into the right direction it will result into reduction in the total fuel consumption by almost 14%. The waste heat from the exhaust gases can be consumed to heat and generate steam which in turn can be used for heating cargo area, accommodation, fuel oil etc.
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation: Under this system, NOx emissions from the engine is lessened by recirculation of exhaust gas from engine cylinder with the scavenge air which lowers the temperature of the combustion chamber. Some part of the exhaust air is re-circulated and added to scavenge air of the engine which lessens the oxygen content of the scavenge air along with temperature of combustion cylinder. With this system NOx reduction up to 80% can be accomplished.
- Water in Fuel: The addition of water in fuel just before its injection into the combustion chamber can reduce the temperature inside the cylinder liner. An efficient system for this can result in NOx reduction of up to 30-35%.
- Improved Pump and Cooling Water System: An optimized cooling water system of pipes, coolers and pumps can develop in decreased resistance to the flow. This will drive towards to the savings of up to 20% of electric power of the ship and fuel consumption up to 1.5 %.
- Sail and Kite Propulsion System: Sail and Kite propulsion system when used along with the conventional propulsion system can lessen the fuel as well as NOx, SOx and CO2 emissions by 35%.
- Fuel and Solar Cell Propulsion: The fuel cell propulsion uses power from a combination of fuel cells, solar cells and battery systems. This helps in lessening of the GHG emission to a very far extent.
- Sandwich Plate System (SPS): It is a system of composting two metals plates by combining it with polyurethane elastomer core. This bypasses usage of steel which requires additional stiffening hence making the structure light weight and less prone to corrosion. This system can definitely play a better role in green ship recycling process as SPS eature includes superior in service performance and reduced through life maintenance.
Conclusion
Through this article we have tried to list the systems and technologies which may help to promote Green Ships. Though it cannot be promoted unless and until its demand in the industry is raised.